Introduction
Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. is a well-known Japanese multinational automaker with its headquarters located in Yokohama, Japan. It is noted for its innovation, quality, and dependability. The firm offers a wide range of vehicles to suit drivers of various tastes and price ranges, including solid sedans, economical SUVs, and iconic sports cars like the Nissan GT-R.
With performance divisions like Nismo and Autech demonstrating its engineering prowess, Nissan operates under both its flagship Nissan brand and the luxury Infiniti brand. Nissan continues to be a global leader in influencing the direction of mobility while respecting its heritage from the early 20th century by pioneering developments in electric vehicles with products like the Nissan LEAF.
Current Services
Nissan’s dedication to the future of transportation is demonstrated by the range of cutting-edge services it provides. Nissan, a leader in electric cars (EVs), offers the all-electric e-NV200 van and the internationally recognised Nissan LEAF. Additionally, the corporation offers energy solutions such as the EV Energy Ecosystem, which includes energy storage devices and home chargers, and Nissan Energy Share, which assists governments and businesses in managing the energy from EVs. These programs demonstrate Nissan’s goal of developing an environmentally responsible and sustainable transportation system.
Apart from electric vehicles, Nissan is a leader in autonomous driving and Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS). With features like ProPILOT Assist and collision avoidance systems, Nissan hopes to improve road safety and lower the number of avoidable collisions. The business keeps experimenting with autonomous driving technology with Nissan’s vision of self-driving cars is further advanced by prototypes like the LEAF. Nissan is committed to increasing EV range and efficiency, as seen by its plans to introduce all-solid-state batteries by 2028.
Additionally, Nissan offers connected technology and mobility services to enhance convenience and transportation. Nissan creates more intelligent transportation solutions by combining EVs and connected car technology through initiatives like Namie Smart transportation. In order to keep drivers informed and engaged, its linked systems include capabilities including over-the-air software updates and remote diagnostics. The company’s Nissan Intelligent Mobility concept, which integrates electric, connected, and autonomous technology into well-known models like the Rogue, Altima, and Ariya EV, is in line with these developments.
Nissan serves both business customers and performance fans in addition to passenger cars. Trucks and vans are delivered by the Nissan Commercial Vehicles sub-brand including the NV-Series and Titan. Meanwhile, Nissan’s Nismo division develops high-performance cars like the GT-R Nismo and 370Z Nismo, reflecting its motorsport heritage. Partnerships with Mitsubishi and other automakers allow Nissan to develop kei cars and expand its global reach. Through innovation in technology, design, and mobility, Nissan continues to shape the future of the automotive industry.
History of Nissan
The origin of the Datsun brand is found in 1911, when Masujiro Hashimoto opened the Kwaishinsha Motor Car Works in Tokyo. In 1914, the firm produced its first car, the DAT, named after its financiers: Kenjiro Den, Rokuro Aoyama, and Meitaro Takeuchi. Over the next several decades, the firm experienced many transformations, including merging with Jitsuyo Jidosha in 1926 to form DAT Jidosha Seizo Co.
In 1931, DAT introduced the Datsun Type 11, originally named “Datson” to refer to “Son of DAT.” Later, however, the company shortened it to “Datsun” because the word “son” had a Japanese pronunciation approximating “loss.” In 1933, with Nissan Group’s takeover, the company shifted its location to Yokohama, cementing its position in Japan’s auto industry.
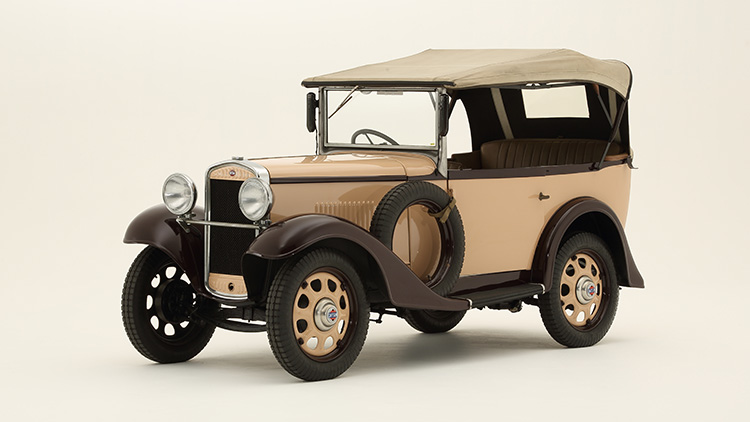

Nissan name entered officially in the 1930s with Nihon Sangyo (Japan Industries), which was founded by Yoshisuke Aikawa. Nissan moved into the business of car manufacturing after the merger of DAT Jidosha Seizo with Tobata Casting in 1933. The company was officially formed and became Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. in 1934. While under the guidance of Aikawa, Nissan ordered its Yokohama plant in 1935 and ventured into truck, car, and airplane engine manufacturing for the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II. In this period, Nissan also engaged in the production of licensed designs, such as in collaboration with the Graham-Paige Company in the USA.
Post-war, Nissan utilized technological advancement and partnerships to become global. Its partnership with the Austin Motor Company in 1952 benefited Nissan by enabling it to produce and market Austins within Japan and towards developing its own engines. Throughout the 1960s, the company introduced the Datsun 510 and 240Z, earning worldwide recognition for innovation and performance.
The 1966 merger with Prince Motor Company brought the legendary models the Skyline and Gloria into Nissan’s lineup. These innovations, combined with expanded production capability in Mexico and the United States, earned Nissan success worldwide, especially during the fuel-efficient car craze of the 1970s.

Nissan partnered with Renault in 1999 to combat financial issues. Under the guidance of CEO Carlos Ghosn, the automaker staged a dramatic turnaround, recording record profits and revamping its model line. The partnership was rocked, however, by Ghosn’s arrest in 2018 on charges of financial impropriety, leading to significant leadership changes. Despite adversity, Nissan remains a dominant force in the global automobile market, with recent moves to restructure its alliance with Renault and expand its presence in electric vehicles and overseas markets.
Revenue
Nissan’s nine-month FY2024 revenue totaled ¥9,143.2 billion, down slightly from the ¥9,171.4 billion reported in the corresponding nine months of FY2023, down by ¥28.2 billion. This was due to reduced vehicle sales, increased sales incentives, and the impact of inflation. But for Q3 FY2024, Nissan saw a modest improvement, with quarterly revenue rising to ¥3,159.0 billion from ¥3,108.1 billion in Q3 FY2023, up by ¥50.9 billion. This reflects a temporary recovery in the second half of the year.
Year over year, Nissan’s total revenue (TTM in USD) for 2024 was $86.45 billion compared to slightly lower $86.48 billion in 2023. Even as the growth in Q3 revenue indicates some positive momentum, year-over-year revenue flattening reflects underlying concerns such as less demand and inflationary forces. Overcoming these will be crucial to Nissan sustaining long-term growth and profitability.
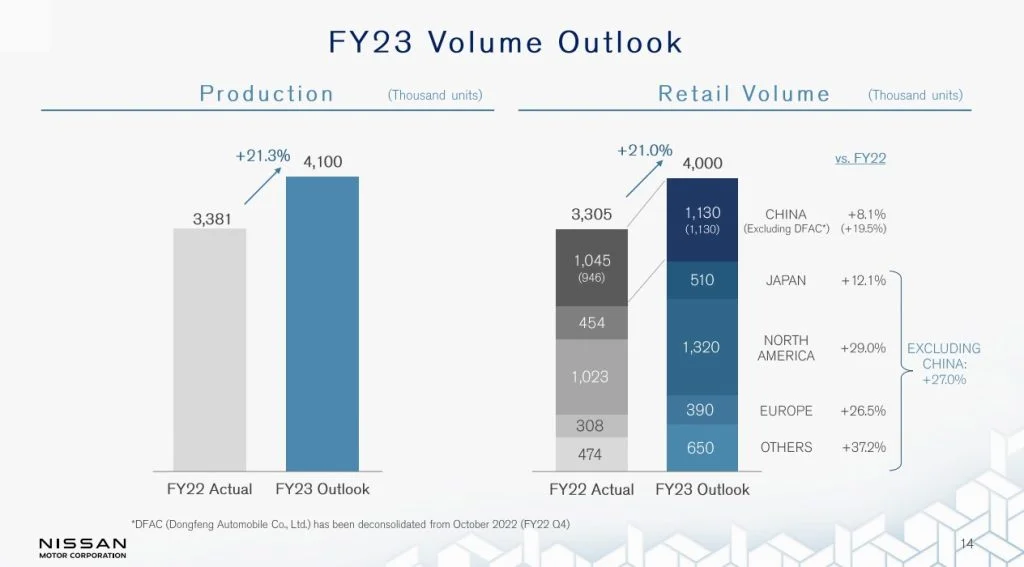
Nissan’s FY2023 volume forecast was superior to FY2024. The company’s net revenue in the first nine months of FY2023 was ¥9,171.4 billion, which was slightly superior to FY2024’s nine-month revenue of ¥9,143.2 billion, which declined by ¥28.2 billion year-over-year. This decline in revenue in FY2024 is due to a slowdown in unit sales, increased sales incentives, and inflationary pressures on overall performance.
Despite this, FY2023‘s improved levels of revenue indicate Nissan experienced greater sales volume during the period. The comparative strength in FY2023 revenue also reflects better market conditions and relatively consistent demand for Nissan products. Going forward, Nissan will need to strive to address issues such as falling sales volumes and inefficiencies in costs to restore its revenue trajectory and boost profitability.
Also Read: Liang Wenfeng’s Heroic Homecoming: DeepSeek Founder Sparks Celebrations in Hometown Amid AI Triumph
Branding and Corporate Identity
Nissan has a number of brands to cater to different markets and segments of buyers. The main Nissan brand is sold globally, and Datsun, which was re-launched in 2013 for emerging markets, was discontinued in 2022 due to poor sales. Infiniti, established in 1989, is the luxury car division of Nissan and has undergone several strategic changes, one of which is its relocation to Hong Kong in 2012. Nismo, the motorsport division of Nissan, has been redirected as the performance brand of the company, emphasizing high-performance and tuning capabilities.
Previously, Nissan’s Japanese dealer network had distinct sales channels in the form of Blue Stage and Red Stage selling specific types of vehicles and price points. Over time, Nissan merged these channels and started retailing badge-engineered cars in all its dealerships. Nissan has also reshaped its corporate identity a few times, adding new logos in order to remake its image, with the current redesign being rolled out in 2020 when it introduced the Ariya electric vehicle.
Achievements and Success
Nissan has received a number of high-profile awards and accolades for its diversity, inclusivity, and work-life balance efforts over the last few decades. Nissan has been consistently praised for their work in creating a healthy and inclusive culture for employees, particularly through their gender equality and LGBT inclusion efforts. The following is an overview of Nissan’s most important achievements and awards in this regard.
Key Achievements and Awards:
- Gold in PRIDE Index (2024-2017): Nissan has achieved Gold in the PRIDE Index annually from 2017 to 2024 for its in-workplace programs in favor of the LGBT community.
- Great Place to Work Certification (2019-2023): Nissan Canada has been certified as a “Great Place to Work” every year from 2019 to 2023 for having a good work environment.
- Eruboshi Certification (2017): Nissan received Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare’s highest “Three-star” Eruboshi certification for promoting women’s participation in the workforce.
- Nadeshiko Brand Recognition (2013-2017): Nissan was annually selected as part of the exclusive “Nadeshiko Brand,” an honor recognizing companies that demonstrate outstanding performance in promoting women.
- Government and Diversity Awards: Nissan has garnered many national awards, including the Government of Japan’s Diversity Award in 2015 and the Catalyst Award for advancing women in business in 2008.
- Introduction of Child-care Centers (2008-2013): Nissan set up various child-care centers in Japan, providing good support to employees with family.
- Work-Life Balance Initiatives: Nissan launched tele-working, abbreviated working hours, and maternal child-care leave to improve the work-life balance of employees, for which it was awarded the Tele-work Promotion Award and the Nikkei Child-Raising Support Award.
Nissan’s continuous efforts to create a diverse, inclusive, and supportive work environment have been recognized by various national and international bodies, further cementing its reputation as an employer of choice.
Conclusion
In short, Nissan Motor Co. Ltd. is a global number one in the automotive industry for its sustainability, innovation, and driving excellence through its vehicles. With a wide variety of sedans, compact vehicles, SUVs, sports vehicles, minivans, kei vehicles, light commercial cars, and components, Nissan strives to enhance human life by making a sustainable future a reality through innovation with technology and eco-friendly, economically feasible, safe, and convenient solutions.
Revenues of approximately ¥10.9 trillion in the fiscal year 2023 demonstrate the strong market presence of the company coupled with strategic operations around the world.
Nissan possesses a large production network across the globe with major manufacturing plants in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Americas, Africa, and Europe. Nissan has strategic locations for its production and research centers with high-profile manufacturing plants in Japan, China, America, and Europe to supply growing demand for vehicles from all over the world.
Nissan’s commitment to building diversity, inclusion, and a strong organizational culture is reflected through numerous awards, including awards in the PRIDE Index, Nadeshiko Brand, and diversity-related certifications. By these efforts, Nissan is constantly innovative and setting the pace in high standards within the automotive industry, becoming one of the primary drivers of mobility’s future shape.









