Introduction
Carvana Co. is revolutionizing the way people buy and sell used cars in the United States. Founded in 2012 and headquartered in Tempe, Arizona, Carvana has transformed the traditional car-buying experience into a seamless online journey. The company’s e-commerce platform empowers customers to browse, research, and purchase vehicles from the comfort of their homes, making car shopping faster, easier, and more transparent.
With innovative features like 360-degree vehicle imaging, Carvana ensures every customer gets a close-up, interactive view of their chosen car. The platform also provides flexible financing options, warranty coverage, and a smooth delivery process. Buyers can either have their car delivered to their doorstep or pick it up from one of Carvana’s iconic car vending machines.
Beyond retail, Carvana operates auction sites, connecting sellers and buyers in the used-car market. This multifaceted approach has positioned the company as a key player in the automotive e-commerce industry. By blending technology, convenience, and customer focus, Carvana Co. continues to reshape the future of car ownership.
Company History and Establishment

The Evolution of Carvana Co.: A Timeline of Milestones and Turning Points
Carvana Co. has grown from a bold idea into a revolutionary force in the automotive e-commerce space. Founded in 2012 by Ernest Garcia III, Ryan Keeton, and Ben Huston, the company set out to redefine how people buy and sell used cars. Here’s a closer look at Carvana’s history, key milestones, and transformative moments.
2012: The Foundation
Carvana was established with financial backing from Drive Time, a leading used car retailer and finance company. The vision was to simplify car buying with an entirely online platform.
2013: The Car Vending Machine Concept
Carvana introduced its first prototype car vending machine, a novel idea that captured public imagination and set the stage for the company’s branding.
2015: A Game-Changing Launch
In Nashville, Tennessee, Carvana unveiled a fully automated coin-operated car vending machine, the first of its kind in the world. This bold move demonstrated the company’s commitment to innovation and established its reputation for redefining the car-buying experience.
2017: Going Public and Major Acquisitions
Carvana made its debut on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker CVNA, marking a significant milestone in its journey. The same year, Carvana acquired Calypso, a rival automotive startup, to bolster its vehicle data and analytics capabilities. Recognition came as Carvana’s co-founders were featured in Fortune’s 40 Under 40 list.
2018: Embracing Cutting-Edge Technology
Carvana purchased Car360, a startup specializing in 3D imaging and augmented reality, for $22 million. This acquisition strengthened Carvana’s platform, allowing customers to view vehicles in greater detail using innovative technology.
2020: Adapting to the Pandemic
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, Carvana introduced touchless delivery and pick-up, addressing safety concerns while maintaining convenience. The company experienced a 25% surge in vehicle sales in Q2 2020, reporting $1.12 billion in revenue, as physical dealerships struggled during the pandemic. By the end of the year, Carvana sold 244,111 vehicles, generating $5.587 billion in revenue, solidifying its position as the second-largest online used car retailer in the U.S.
2022: Expanding Reach with ADESA
Carvana made a bold move by acquiring ADESA, the nation’s second-largest wholesale auto auction chain, for $2.2 billion. This acquisition significantly expanded Carvana’s operational footprint and strengthened its logistical capabilities.
2023: Introducing Same-Day Delivery
Carvana launched same-day delivery, initially rolling out the service in select markets, including Alabama, Arizona, North Carolina, and Dallas-Fort Worth. This move underscored the company’s commitment to speed and customer convenience.
2024: A Turnaround Year
Amid challenges, including layoffs and a steep stock decline, Carvana undertook a major restructuring over 18 months. The company introduced Carli, proprietary software for end-to-end vehicle reconditioning, along with tools for logistics optimization and AI-driven workflows. These changes helped Carvana streamline operations, cut costs, and position itself for a sustainable future.
Present and Future
Carvana now operates 30+ vending machines, serves 300+ markets, and continues to expand its innovative services. Despite challenges, its focus on technology, customer experience, and efficiency drives its vision to redefine automotive e-commerce. With a legacy of overcoming obstacles and embracing innovation, Carvana remains a key player shaping the future of car retail.
Business Model and Innovations: How Carvana Earns Money?
With a mission statement “To change the way people buy cars by providing our customers a car-buying solution that is fun, fast, fair, and powered by technology.”
Carvana operates a retail-centric business model, combining innovative technology with customer convenience to redefine the used-car market. By selling directly to consumers and leveraging online tools, Carvana eliminates traditional dealership overhead, allowing it to focus on competitive pricing, streamlined processes, and exceptional customer experiences. Here’s how Carvana generates its revenue:
Retail Used-Car Sales: Core Revenue Driver
Retail sales form the backbone of Carvana’s business, contributing 77.3% of its total revenue in 2021, amounting to $9.9 billion. The company sources vehicles through trade-ins, auctions, and direct purchases, adds costs for inspection, maintenance, and logistics, and sells them at a markup.
Using Carvana’s user-friendly app or website, customers can browse available cars with advanced 360° imaging technology, offering a virtual experience to inspect vehicles and even simulate a test drive. Taxes, registration fees, and title costs are transparently included in the final pricing. Carvana’s retail platform ensures convenience and builds trust, fostering loyalty and repeat purchases.
Wholesale Car Sales: A Secondary Revenue Stream
Excess inventory and cars failing Carvana’s strict retail quality checks are sold through its CarvanaACCESS platform, targeting wholesale buyers and dealerships. This segment accounted for $1.9 billion in revenue in 2021. Wholesale operations reduce overhead costs, as these vehicles require minimal inspection or preparation, offering higher profit margins.
Customer-Centric Approach
Carvana’s business model emphasizes customer convenience. Buyers can set alerts for unavailable vehicles, schedule home deliveries, or pick up their purchase from the iconic Car Vending Machines. The seamless integration of technology ensures a hassle-free purchasing process.
Operational Innovations for Profitability
Carvana’s model integrates technology to control costs and enhance scalability. Revenue is amplified through competitive pricing strategies and reduced operational friction. Innovations like 360° imaging and touchless delivery have made Carvana a preferred choice for modern car buyers.
Strategic Moves From the Company
Carvana’s journey has been defined by strategic innovations and market adaptability, shaping its position as a leader in the online used-car retail industry. A major breakthrough came early on with the introduction of its iconic car vending machines, which transformed the traditional car-buying experience and cemented the brand’s identity.
The company’s public debut in 2017 marked another significant milestone, providing the financial backing needed for expansion and innovation. This period also saw strategic acquisitions, such as Car360 and Calypso, which integrated advanced imaging and data analytics into Carvana’s operations, enhancing its customer-centric platform.
The COVID-19 pandemic presented both challenges and opportunities for Carvana. With physical dealerships shuttered, the company’s touchless delivery service gained immense traction, leading to a sharp increase in sales and revenues. However, the post-pandemic period brought hurdles, including declining consumer demand and rising operational costs.
To combat these, Carvana implemented a sweeping restructuring plan. By cutting costs, reducing headcount, and deploying AI-powered tools like Carli for logistical and operational efficiency, the company signaled its shift from rapid expansion to sustainable growth.
Another transformative move was the acquisition of ADESA in 2022, which significantly bolstered Carvana’s logistics and reconditioning infrastructure, positioning the company for long-term scalability. As of 2024, Carvana’s commitment to innovation and resilience remains evident in its adoption of generative AI and streamlined processes, showcasing its ability to adapt to evolving market demands while staying focused on operational excellence.
Related: Walmart – Company Analysis, History, Success, Net Worth, Yearly Revenue
Carvana’s Channels: Bridging Convenience with Technology
Carvana’s distribution channels are designed to ensure accessibility and seamless user experiences, catering to modern customers who prioritize convenience and efficiency. These channels integrate advanced technology with user-friendly interfaces, enabling buyers, sellers, and trade-in dealers to interact effortlessly with the platform.
Website: The Digital Hub of Operations
Carvana’s website serves as the primary platform for all its operations. Buyers can browse vehicles, sellers can list their cars, and trade-in dealers can complete transactions—all within a few clicks. In addition to car purchases, the website offers essential services like vehicle financing, warranty options, and insurance coverage. With its intuitive design and feature-rich interface, the website acts as the backbone of Carvana’s e-commerce ecosystem.
Mobile Applications: Convenience On-the-Go
Carvana extends its reach through mobile apps available for both Android and iOS devices. The app mirrors the features of the website, offering services like vehicle searches, financing, trade-ins, and delivery tracking. With the app, users enjoy on-the-go access to Carvana’s services, making the entire process – from browsing to purchase – hassle-free. The mobile-first strategy underscores Carvana’s commitment to providing convenience for tech-savvy customers.
Seamless Integration Across Platforms
Whether on the website or mobile app, Carvana ensures a consistent experience. Advanced tools like 360° imaging, instant loan approvals, and real-time vehicle availability updates are available across all channels, making transactions both transparent and efficient.
By leveraging these digital channels, Carvana aligns with the preferences of today’s consumers, offering a simplified and technology-driven approach to buying and selling vehicles.
Carvana’s Financial Performance Analysis: Q2 Results and Projections for 2024
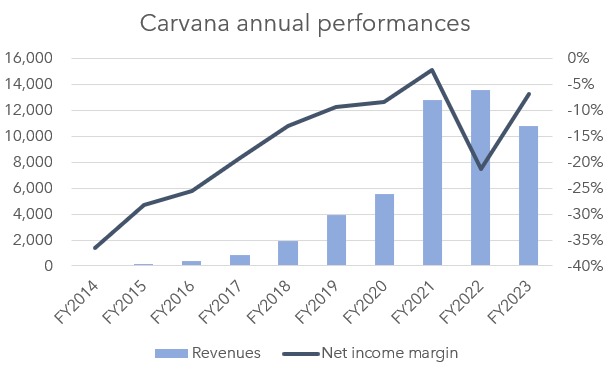
Carvana has showcased a remarkable financial turnaround, delivering strong Q2 results for 2024 and providing an optimistic outlook for the year. The company has defied prior market concerns of bankruptcy, signaling its resilience and growth potential. Below is a detailed analysis of Carvana’s recent performance and future financial expectations.
Earnings and Revenue Beat Expectations
Earnings Per Share (EPS): Reported a profit of 14 cents compared to an expected loss of 7 cents, showcasing a substantial improvement in profitability.
Revenue: Achieved $3.41 billion, surpassing the expected $3.24 billion, reflecting strong operational execution and demand.
Growth in Retail Vehicle Sales
Retail sales surged by 32.5% year-over-year, with more than 101,400 vehicles sold during the quarter. This reflects the growing consumer preference for Carvana’s services.
Profitability Metrics
Gross Profit Per Unit (GPU): Reached a record of $7,049, marking an increase of $529 from the prior year. This improvement was driven by better pricing, cost efficiencies, and strong retail demand.
Net Income and Margin: Reported a net income of $48 million with a 1.4% net income margin, a notable turnaround from previous losses.
Adjusted EBITDA Performance
Q2 Adjusted EBITDA was $355 million with a margin of 10.4%, setting new company records. Carvana’s full-year 2024 adjusted EBITDA is projected to range between $1 billion and $1.2 billion, a significant leap from $339 million in 2023.
Strategic Developments and Outlook
Capital Raise
Announced an at-the-market stock offering of approximately $1 billion, equating to 35 million shares. This move strengthens liquidity and supports future growth initiatives.
Growth Trajectory
Sequential growth in retail vehicle sales is expected for Q3 2024, driven by robust demand and operational improvements.
Carvana’s third consecutive year of EBITDA profitability is anticipated, signaling strong financial health and effective cost management.
Leadership Confidence
CEO Ernie Garcia emphasized the company’s untapped potential and long-term growth opportunities in a shareholder letter.
Turnaround Success
Carvana’s Q2 2024 results mark a significant shift from the challenging financial outlook it faced in early 2022. Strong profitability, record margins, and operational efficiency reflect the success of its restructuring efforts.
Future Prospects and Risks
Carvana’s strong guidance and strategic initiatives place it on a growth trajectory. However, reliance on market dynamics, including demand for used vehicles and macroeconomic conditions, remains a key risk factor. The company’s ability to sustain profitability while navigating industry challenges will determine its long-term success.









